Intraday trading can be a challenging task for many traders. The market can be volatile, and prices can fluctuate rapidly, making it difficult to identify the best entry and exit points. Moving averages (MAs) are one of the most popular and effective technical indicators used by traders to identify trends and potential trade opportunities. In this article, we will explore what moving averages are, how they work, and how you can use them in your intraday trading strategy.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Are Moving Averages?
- Types of Moving Averages
- Simple Moving Average (SMA)
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
- Weighted Moving Average (WMA)
- How Moving Averages Work
- How to Use Moving Averages for Intraday Trading
- Identifying Trends
- Finding Entry and Exit Points
- Using Multiple Moving Averages
- Tips for Using Moving Averages in Intraday Trading
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Moving Averages
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Are Moving Averages?
A moving average is a widely used technical indicator that helps traders identify trends and potential trade opportunities. It is a mathematical calculation that averages the prices of an asset over a specific period of time. The resulting line represents the smoothed-out average price of the asset over that time period. Moving averages are called “moving” because they are continually recalculated as new data becomes available, creating a line that moves on the chart.
Types of Moving Averages
There are three main types of moving averages: simple moving average (SMA), exponential moving average (EMA), and weighted moving average (WMA).
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
A simple moving average is calculated by adding the closing prices of an asset for a specific number of time periods and then dividing the total by the number of periods. For example, a 10-day SMA would add up the closing prices for the last 10 days and divide that number by 10.
Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
An exponential moving average gives more weight to recent prices and less weight to older prices. This is achieved by applying a smoothing factor to the calculation. The smoothing factor used is typically a percentage of the previous EMA value. This means that the EMA will react more quickly to price changes than the SMA.
Weighted Moving Average (WMA)
A weighted moving average is similar to a simple moving average, but it gives more weight to recent prices. This is achieved by multiplying each price by a weight factor, which is based on the number of time periods being used in the calculation.
How Moving Averages Work
Moving averages are used to smooth out price fluctuations and identify trends. When the price is above the moving average line, it is considered an uptrend, and when the price is below the moving average line, it is considered a downtrend. The longer the time period used to calculate the moving average, the smoother the line will be.
How to Use Moving Averages for Intraday Trading
Moving averages can be used in various ways in intraday trading. Here are some ways to use them effectively:
Identifying Trends
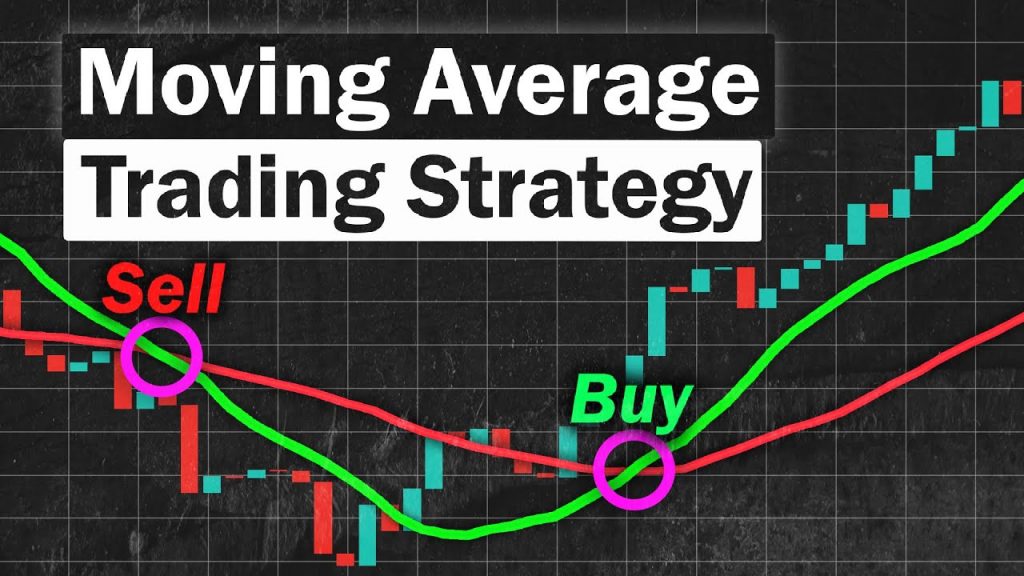
One of the most popular uses of moving averages is to identify trends. Traders can use a moving average to determine whether the market is in an uptrend, a downtrend, or a range. If the price is above the moving average line, it is considered an uptrend, and if the price is below the moving average line, it is considered a downtrend. Traders can also use multiple moving averages to identify trend reversals.
Finding Entry and Exit Points
Moving averages can also be used to identify potential entry and exit points. When the price is above the moving average line, traders may look for buying opportunities, and when the price is below the moving average line, traders may look for selling opportunities. However, traders should be cautious as the price can often break through the moving average line, indicating a change in the trend.
Using Multiple Moving Averages
Traders can use multiple moving averages to increase the accuracy of their trading signals. The most popular method is to use two or more moving averages with different time periods. For example, a trader may use a 20-day and a 50-day moving average. When the shorter-term moving average (20-day) crosses above the longer-term moving average (50-day), it is considered a bullish signal. On the other hand, when the shorter-term moving average crosses below the longer-term moving average, it is considered a bearish signal.
Tips for Using Moving Averages in Intraday Trading
Here are some tips for using moving averages effectively in intraday trading:
- Use multiple moving averages to confirm the trend
- Use a combination of short-term and long-term moving averages
- Choose the time period that best suits your trading style
- Combine moving averages with other technical indicators
- Use stop loss orders to manage risk
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Traders often make the following mistakes when using moving averages:
- Using moving averages as the sole indicator
- Using moving averages with a short time period
- Ignoring the current market conditions
- Not using stop loss orders
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Moving Averages
Advantages:
- Easy to use and understand
- Helps identify trends and potential trade opportunities
- Can be used in conjunction with other technical indicators
Disadvantages:
- Can produce false signals in ranging markets
- Lagging indicator, which means it may not always provide timely signals
- Can produce whipsaws (a false signal followed by a reversal)
Conclusion
Moving averages are a popular and effective tool used by traders to identify trends and potential trade opportunities. By understanding how moving averages work and how to use them in your intraday trading strategy, you can increase your chances of success in the market.
FAQs
- Can moving averages be used for long-term trading? Yes, moving averages can be used for long-term trading as well as intraday trading.
- What is the best time period for a moving average? The best time period for a moving average depends on the trading style and the asset being traded. Short-term traders may use a shorter time period, while long-term traders may use a longer time period.
- Can moving averages be used in conjunction with other technical indicators? Yes, moving averages can be used in conjunction with other technical indicators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator.
- Do moving averages work in all market conditions? No, moving averages may not work effectively in ranging markets, as they tend to produce false signals.
- How can I avoid false signals when using moving averages? Traders can avoid false signals by using multiple moving averages and confirming the trend with other technical indicators. Additionally, using stop loss orders can help manage risk and prevent significant losses.